Logistics Definition and Its Impact on Machine Vision

Logistics involves planning and executing the movement of resources to ensure timely delivery at an optimal cost. It plays a critical role in industries by streamlining operations and reducing inefficiencies. With the global logistics market expected to grow from $8.96 trillion in 2023 to $15.79 trillion by 2028, advancements in technology are reshaping this sector. One of the most transformative innovations is the Logistics machine vision system. This technology uses cameras and algorithms to automate processes, improve accuracy, and enhance efficiency, making logistics smarter and faster.
Key Takeaways
- Logistics helps move and store goods quickly and cheaply.
- Machine vision uses cameras to do tasks better than humans.
- It saves money by cutting labor costs and checking quality.
- New ideas like AI and IoT make logistics smarter and greener.
- Even with problems, machine vision boosts work speed and decisions.
Logistics Definition and Historical Context
What Is Logistics?
Logistics refers to the process of planning and executing the efficient movement and storage of goods, services, or information from their origin to their destination. It ensures resources are delivered on time and at the lowest possible cost, meeting customer needs effectively. You encounter logistics daily, whether through online shopping or the delivery of essential goods.
Here’s how logistics is defined by leading sources:
| Source | Definition |
|---|---|
| TechTarget | Logistics is the process of planning and executing the efficient transportation and storage of goods from the point of origin to the point of consumption. The goal of logistics is to meet customer requirements in a timely, cost-effective manner. |
| The Dictionary of Transport and Logistics | Provides a comprehensive reference for terminologies, abbreviations, and acronyms relevant to the fields of transport and logistics, covering a wide range of topics including supply-chain management and transport policy. |
These definitions emphasize the critical role logistics plays in ensuring smooth operations across industries.
Evolution of Logistics Over Time
The logistics industry has undergone significant transformations over the centuries. Each milestone has shaped the way goods are transported, stored, and delivered.
- Statistical methods, such as linear regression, have helped professionals analyze historical data to optimize operations.
- The Industrial Revolution introduced steam power and mechanization, revolutionizing production and transportation.
- Railways in the 19th century increased trade volumes and improved logistics planning through timetabling.
- World Wars I and II drove advancements in supply chain management and inventory control, laying the foundation for modern logistics.
- Standardized shipping containers, introduced in the 1950s, increased efficiency and enabled intermodal transportation.
- The internet and e-commerce transformed logistics in the late 20th century, enabling real-time tracking and last-mile delivery.
These developments highlight how logistics has evolved to meet the growing demands of global trade and technology.
Importance of Logistics in Modern Industries
Logistics is the backbone of modern industries. It ensures products reach consumers efficiently, supports global trade, and drives economic growth. Without logistics, businesses would struggle to meet customer expectations or compete in the global market.
Here are some key statistics that demonstrate the importance of logistics:
| Statistic | Description |
|---|---|
| Growth Rate | Logistics is expected to be the fastest-growing industry between 2023–2030. |
| Employment | The UK logistics industry employs around 1.25 million people. |
| Market Size | The US freight and logistics market size is expected to reach 1.62 trillion USD by 2029. |
| Tracking Implementation | At least 50% of companies in all subsectors have freight tracking in place. |
| Visibility Goals | 70% of organizations have real-time supply chain visibility as a top strategic goal. |
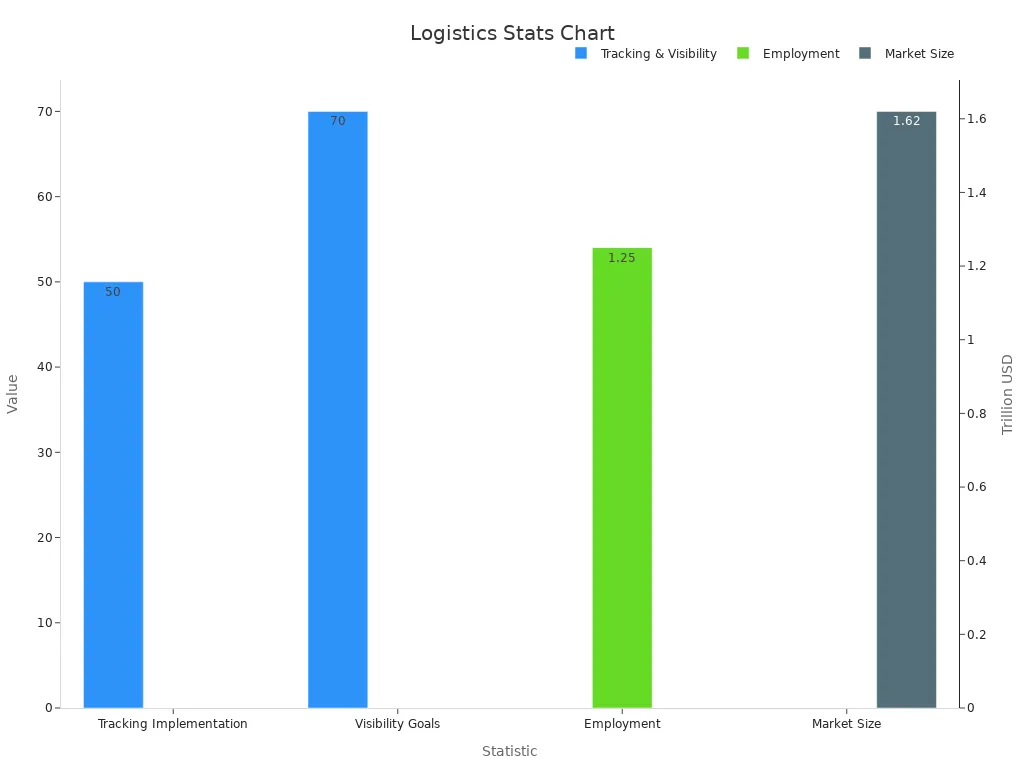
These figures highlight the logistics industry's rapid growth and its critical role in supporting businesses worldwide. As you can see, logistics is not just about moving goods; it’s about creating value and driving innovation.
Core Functions of Logistics
Transportation and Distribution
Transportation and distribution form the backbone of logistics. These functions ensure goods move efficiently from manufacturers to consumers. You rely on transportation systems daily, whether receiving packages or purchasing products in stores. Optimizing these systems requires analyzing performance metrics to improve delivery speed and accuracy.
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| On-Time Final Delivery | Measures a carrier’s ability to deliver on the scheduled date, impacting costs and delivery efficiency. |
| Cost Per Pound | Assesses gross net with total weight moved, helping to identify buying patterns and optimize costs. |
| Inventory Accuracy | Evaluates the accuracy of orders pulled from the warehouse, crucial for customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. |
| On-Time Shipping | Indicates the percentage of shipments leaving the warehouse on time, essential for meeting customer expectations. |
| Order Accuracy | Records the accuracy of filled orders, directly affecting customer satisfaction and operational costs. |
| Fill Rate | Measures the ability to fill orders from a specific distribution center, impacting backorders and delays. |
Quantitative analyses play a vital role in transportation and distribution. They transform logistics data into actionable insights, helping you optimize routes, predict equipment failures, and reduce costs. These data-driven decisions enhance efficiency and improve customer satisfaction.
Warehousing and Inventory Management
Warehousing and inventory management ensure goods are stored securely and tracked accurately. Efficient systems prevent stockouts and overstocking, which can lead to lost revenue. However, challenges like outdated equipment and insufficient space often hinder operations.
| Challenge | Percentage | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Attracting and finding a qualified workforce | 59% | Statista |
| Insufficient space for inventory | 36% | Statista |
| Outdated equipment | 36% | Statista |
| Poor information systems support | 21% | N/A |
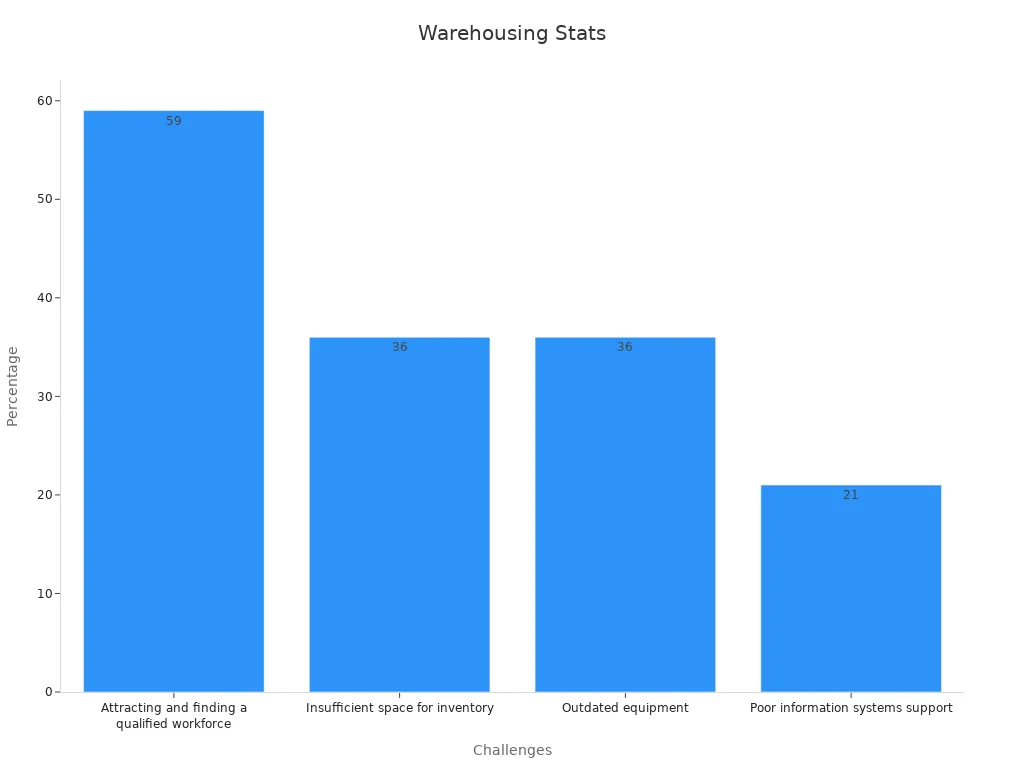
Nearly 43% of small businesses fail to track inventory or rely on manual systems, leading to inefficiencies. Poor inventory management can cause businesses to lose up to 11% of annual revenue. By adopting modern systems, you can improve accuracy and streamline operations, ensuring your logistics processes remain competitive.
Resource and Supply Chain Management
Resource and supply chain management focus on coordinating materials, information, and finances across the global supply chain. These functions aim to reduce costs, improve quality, and enhance operational speed.
| Metric Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost Metrics | Track expenses throughout the supply chain operation, identifying cost-saving opportunities. |
| Quality Indicators | Focus on accuracy, reliability, and customer satisfaction, measuring order fulfillment quality. |
| Time and Speed Metrics | Evaluate operational velocity, highlighting bottlenecks in supply chain processes. |
Effective supply chain management requires you to monitor these metrics closely. For example, tracking costs helps identify savings opportunities, while quality indicators ensure customer satisfaction. Time and speed metrics highlight inefficiencies, allowing you to address bottlenecks and improve overall performance.
Logistics Machine Vision System
Overview of Machine Vision Technology
Machine vision technology uses cameras, sensors, and algorithms to interpret visual data. It mimics human vision but processes information faster and with greater precision. In logistics, this technology plays a pivotal role in automating tasks and improving operational efficiency.
You can think of machine vision as the eyes of modern logistics systems. It captures images or videos, analyzes them using artificial intelligence (AI), and provides actionable insights. For example, it can detect the size, shape, and condition of packages in real time. This capability ensures that goods are handled correctly and efficiently throughout the supply chain.
Machine vision systems also integrate seamlessly with other technologies, such as robotics and the Internet of Things (IoT). This integration allows you to create smarter warehouses and transportation networks. By leveraging these systems, you can reduce human error, enhance accuracy, and optimize resource utilization.
Applications of Machine Vision in Logistics
Machine vision has transformed logistics by introducing innovative applications that streamline operations. Here are some of the most impactful uses:
- Predictive Maintenance: Identifies early signs of wear in equipment, such as conveyor belts, to prevent costly breakdowns.
- Worker Safety and Hazard Detection: Monitors compliance with safety gear and detects potential hazards in real time.
- Route Optimization: Analyzes traffic data to develop efficient delivery routes, saving time and fuel.
- Automated Checkout: Enhances accuracy in retail logistics by scanning items and preventing fraud.
- Bin Utilization Analysis: Optimizes warehouse space by analyzing how containers are used.
- Perimeter Monitoring: Ensures security by detecting unauthorized access to restricted areas.
- Fall Detection: Quickly identifies staff incidents, enabling faster emergency responses.
- Vehicle Safety: Reduces collision risks between vehicles and pedestrians in busy logistics hubs.
- Real-Time Package Tracking: Tracks packages throughout their journey, ensuring transparency and reliability.
- Drone Delivery: Facilitates timely delivery in hard-to-reach areas, revolutionizing last-mile logistics.
Companies like UPS, Walmart, and Bosch have already adopted machine vision systems. UPS uses them to monitor sorting equipment, while Walmart employs them to enhance worker safety. Bosch leverages visual data for efficient palletizing and packaging. These examples highlight how machine vision is reshaping logistics processes across industries.
Benefits of Machine Vision Integration
Integrating machine vision into logistics offers numerous benefits that enhance both efficiency and profitability. Here’s how it can transform your operations:
- Cost Savings: Automating tasks with machine vision reduces labor costs and minimizes errors. For instance, AI camera systems can inspect parcels for defects, eliminating the need for manual checks.
- Improved Safety: Machine vision monitors warehouse floors and vehicles to prevent accidents. It also detects potential theft, safeguarding your assets and employees.
- Operational Scalability: As your business grows, machine vision systems can handle increased volumes without requiring additional staff. This scalability makes it easier to expand operations.
- Enhanced Quality Assurance: High-resolution cameras detect product defects that human inspectors might miss. This capability ensures higher quality standards and reduces returns or recalls.
- Space Optimization: Camera-based systems analyze the occupancy of storage areas and transport vehicles. This analysis helps you utilize space more efficiently, reducing costs and delays.
- Increased Reliability: AI vision systems monitor equipment conditions, enabling predictive maintenance. This proactive approach enhances operational reliability and minimizes downtime.
By adopting a logistics machine vision system, you can achieve faster processing times, better resource management, and higher customer satisfaction. These benefits make it a game-changer for businesses aiming to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
How Machine Vision Impacts Logistics

Automation and Process Optimization
Machine vision technology revolutionizes logistics by automating repetitive tasks and optimizing processes. You can use it to streamline operations, reduce errors, and improve productivity. For example, automated monitoring systems eliminate human error by continuously tracking inventory and sorting items. This ensures accurate placement decisions and reduces operational costs.
To measure the impact of automation, you can evaluate key metrics:
- Identify relevant KPIs for each business purpose.
- Compare revenue generated by manual, semi-automated, and fully automated setups.
- Continuously review Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for visibility.
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Inventory Visibility | Enhances tracking of stock, reducing loss and assortment shortages. |
| Sorting Automation | Simplifies the classification of items, allowing for efficient placement decisions. |
| Inspection Efficiency | Automates defect detection, freeing employees for higher-value tasks. |
| Movement Analysis | Identifies bottlenecks and improves employee effectiveness through gesture recognition. |
| Automated Monitoring | Reduces human error and operational costs through fully automated systems. |
| Space Optimization | Predicts and executes efficient container configurations to maximize space utilization. |
By leveraging these metrics, you can ensure that your logistics processes remain efficient and scalable.
Enhancing Quality Control and Accuracy
Machine vision systems enhance quality control by identifying defects and irregularities during manufacturing and logistics operations. You can rely on these systems to automate inspections, significantly reducing human error and improving product quality. For instance, high-resolution cameras detect flaws that manual checks might miss, ensuring consistent standards.
Metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score evaluate the performance of machine vision systems. Some systems achieve up to 99.4% accuracy, making them highly reliable for quality assurance. Accuracy measures the percentage of correctly classified objects, while precision and recall ensure defects are identified without false positives. These capabilities help you maintain high-quality standards across your logistics operations.
Improving Efficiency and Reducing Costs
Machine vision systems improve efficiency and reduce costs by automating tasks and minimizing errors. For example, Averroes.ai reduced weekly false rejects from 12,000 to 246, saving manufacturers over $18 million annually per production line. Automated inspection systems also decrease labor costs, resulting in annual savings of $691,200.
You can measure efficiency improvements through faster inspection speeds, reduced human error, and real-time feedback. These systems enable consistent quality assurance, which boosts productivity and cost-effectiveness. By adopting machine vision technology, you can optimize freight logistics and e-commerce logistics processes, ensuring your operations remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
The Future of Logistics and Machine Vision
Emerging Trends in Logistics Technology
The logistics industry is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements that enhance efficiency and sustainability. Several trends are shaping the future of logistics:
- Automation and Robotics: Automated systems are streamlining operations, from warehouse management to delivery. Nearly 80% of companies plan to invest in robotics to improve efficiency.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is transforming logistics by optimizing routes and predicting demand patterns. Currently, 72% of logistics firms use AI for operational improvements.
- Blockchain: This technology ensures transparency and security in supply chain transactions, reducing fraud and errors.
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices enable real-time monitoring of shipments, improving visibility and decision-making.
- Sustainability: Companies are adopting eco-friendly practices to reduce carbon footprints, aligning with global environmental goals.
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Automation and robotics | Increasing use of automated systems to enhance efficiency in logistics. |
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | AI applications for route optimization and demand prediction. |
| Blockchain | Enhancing transparency and security in supply chain transactions. |
| Internet of Things (IoT) | Connecting devices for real-time data and monitoring. |
| Sustainability | Focus on eco-friendly practices and reducing carbon footprints. |
| Market Growth | U.S. logistics market projected to reach $1.89 trillion by 2029. |
These trends highlight how technology is reshaping logistics, making it more efficient and sustainable.
Challenges in Adopting Machine Vision
While machine vision offers immense potential, its adoption comes with challenges. Traditional systems often struggle to maintain accuracy in dynamic environments. For instance, frequent changes in packaging or lighting conditions can disrupt performance.
Deep learning models address these issues by adapting to changing production lines without requiring extensive adjustments. However, implementing such systems demands significant investment and expertise. Industries also face hurdles like equipment misalignment and the need for constant recalibration.
Despite these challenges, machine vision remains vital for quality assurance. It helps detect defects and ensures compliance with safety standards. The quality assurance segment holds the largest market share, reflecting the growing reliance on advanced machine vision systems.
Long-Term Benefits of Machine Vision in Logistics
Integrating machine vision into logistics delivers long-term benefits that outweigh initial costs. These systems enhance accuracy and precision, ensuring high product quality. They also operate continuously, inspecting items at high speeds and reducing downtime.
Key advantages include:
- Cost Efficiency: Although initial investments are high, long-term savings from reduced labor costs and fewer defects lower overall expenses.
- Improved Quality Control: Automated inspections ensure consistency and traceability, helping you meet regulatory standards.
- Real-Time Decision-Making: Instant feedback allows for immediate corrective actions, boosting operational responsiveness.
- Enhanced Productivity: Machine vision systems increase efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, freeing up resources for strategic activities.
By adopting machine vision, you can future-proof your logistics operations. These systems not only improve efficiency but also position your business for sustained growth in a competitive market.
Logistics ensures the efficient movement of goods, making it essential for industries worldwide. Machine vision has revolutionized logistics by automating tasks, improving accuracy, and reducing costs. It enables you to optimize processes, enhance quality control, and achieve faster deliveries.
🚀 The future of logistics lies in advanced technologies like AI, IoT, and robotics. These innovations will help you create smarter, more sustainable supply chains. By embracing these tools, you can stay ahead in a competitive market and meet evolving customer demands effectively.
FAQ
What is the role of logistics services in modern industries?
Logistics services ensure the efficient movement of goods from manufacturers to consumers. They handle transportation, warehousing, and inventory management, helping businesses meet customer demands while reducing costs. These services are essential for maintaining smooth operations in global supply chains.
How does machine vision improve logistics operations?
Machine vision automates tasks like package sorting, defect detection, and inventory tracking. It reduces human error, enhances accuracy, and speeds up processes. By using cameras and AI, you can optimize workflows and improve overall efficiency in your logistics operations.
Are machine vision systems expensive to implement?
While initial costs can be high, machine vision systems offer long-term savings. They reduce labor expenses, minimize errors, and improve productivity. Over time, these benefits outweigh the upfront investment, making them a cost-effective solution for logistics.
Can small businesses benefit from machine vision technology?
Yes, small businesses can use machine vision to streamline operations and reduce costs. Affordable solutions like automated inventory tracking and quality control systems help improve efficiency. These technologies allow small businesses to compete effectively in the logistics industry.
What challenges might you face when adopting machine vision?
You may encounter challenges like high initial costs, equipment misalignment, and the need for technical expertise. Frequent changes in packaging or lighting conditions can also affect system performance. However, with proper planning and training, these obstacles can be overcome.
See Also
Exploring Dimensional Measurement Within Machine Vision Technologies
An Overview of Cameras Used in Machine Vision Systems
The Importance of Machine Vision Systems for Volume Assessment
Navigating Equipment Placement in Machine Vision Applications
Understanding Electronic Components in Machine Vision Systems
