Exploring the Basics of Metrology Machine Vision Systems
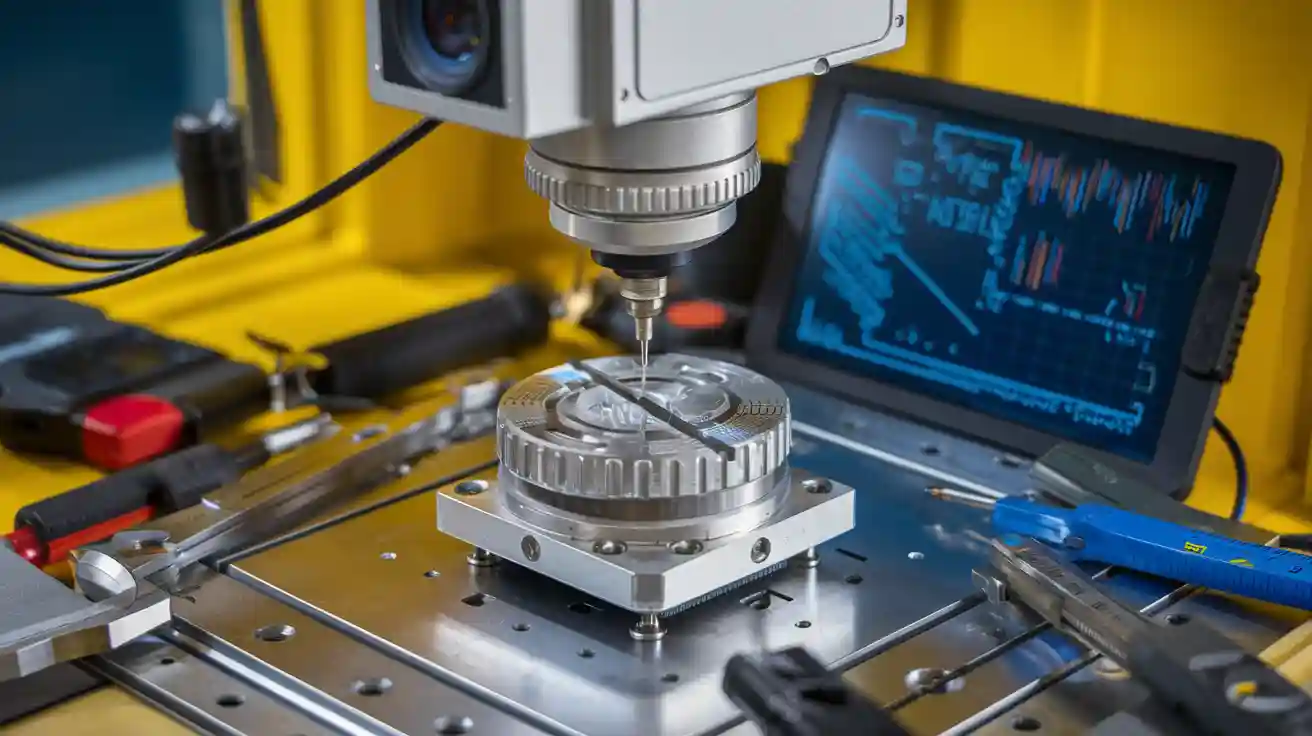

A metrology machine vision system combines advanced imaging technology with precise measurement tools to inspect and measure objects with exceptional accuracy. You can use these systems to automate tasks like dimensional analysis and defect detection, which ensures consistent results and speeds up production.
Modern manufacturing relies on these systems to achieve higher standards of quality control. For example:
- Automated inspection reduces manual intervention while maintaining accuracy and reliability.
- Non-contact methods like laser scanning are at least ten times faster than traditional techniques.
- Artificial intelligence integration automates data analysis, streamlining visual quality control processes.
By adopting this technology, you can measure intricate geometries and verify products with unmatched precision, enhancing productivity and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
Key Takeaways
- Metrology vision systems check items faster and more accurately.
- They use non-touch methods to protect fragile materials and handle tricky shapes.
- Adding AI helps find problems and predict fixes, making work smarter.
- Watching in real-time helps fix issues early, saving time and boosting work output.
- Using these systems meets rules, improves product quality, and cuts down waste.
What Is a Metrology Machine Vision System?
Definition and Core Components
A metrology machine vision system is a technology that combines imaging tools with precise measurement techniques to inspect and analyze objects. These systems are designed to capture detailed images and extract accurate data for quality control and manufacturing processes. Unlike traditional methods, they rely on advanced optics and software to perform non-contact measurements, making them ideal for delicate or complex materials.
To understand how these systems work, you need to know their core components:
- Hardware Components: High-quality cameras, lenses, and lighting systems capture clear and detailed images.
- Software Processes: Algorithms process the images to extract measurements and detect defects.
- Calibration Tools: Regular calibration ensures the system maintains accuracy over time.
- Environmental Controls: Factors like temperature and humidity are monitored to prevent measurement errors.
| Metric | Definition |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | The degree of conformance between a measurement and a recognized standard indicating the true value. |
| Repeatability | The variation in repeated measurements of the same quantity under identical conditions. |
| Resolution | The smallest distinguishable optical feature in an image, influenced by sensor pixels and optics. |
These components work together to deliver reliable and repeatable results, even in challenging environments.
Integration of Metrology and Machine Vision Technologies
The integration of metrology and machine vision technologies has revolutionized manufacturing. By combining precise measurement tools with imaging systems, you can achieve faster and more accurate results. This integration allows for real-time monitoring and automated vision metrology, reducing the need for manual inspections.
For example, in manufacturing, vision-based metrology systems can:
- Detect defects with 99% accuracy.
- Monitor processes in real time to ensure consistency.
- Verify the correct assembly of components.
- Predict equipment failures to minimize downtime.
| Application | Benefit Description |
|---|---|
| Defect Detection | 99% accuracy in identifying defects |
| Safety Monitoring | Automated systems enhance workplace safety |
| Quality Control | Improved precision and consistency in product quality |
| Process Monitoring | Real-time oversight of manufacturing processes |
| Assembly Verification | Ensures correct assembly of components |
This integration also supports advanced techniques like nanoscale imaging, where optical scattering provides critical data for nanoelectronics. By using tools like Cognex’s calibration system, you can convert camera pixels into real-world units, enabling precise in-line measurement.
Key Features and Capabilities
Metrology machine vision systems offer several key features that make them indispensable in modern manufacturing. These include:
- High Precision: Systems can achieve a spatial resolution of 0.001 inch/pixel, ensuring precise measurements.
- Non-Contact Inspection: Ideal for fragile or intricate materials, these systems measure without physical contact.
- Automation: Computer-controlled vision inspection reduces human error and speeds up processes.
- Versatility: They handle tasks like dimensional measurement, defect detection, and assembly verification.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Field Of View | The viewable area of the object, influenced by the camera’s sensor and lens focal length. |
| Working Distance | The distance from the lens to the object, which varies based on application constraints. |
| Resolution | The detail reproduction capability of the imaging system, determined by pixel size and count. |
| Depth Of Field | The maximum object depth that can be kept in focus, important for applications like barcode reading. |
| Sensor Size | The active area size of the camera sensor, affecting the choice of lens and magnification. |
| Primary Magnification | The ratio of sensor size to the field of view, crucial for selecting the appropriate lens. |
These features allow vision measuring machines to perform tasks with unmatched accuracy and efficiency. For example, a system with a tolerance band of 0.01 inch can achieve a precision of +/- 0.005 inch, making it suitable for high-stakes industries like aerospace and electronics.
By adopting automated metrology, you can reduce labor costs, improve product quality, and stay competitive in today’s fast-paced manufacturing environment.
Differences Between Traditional Metrology and Automated Vision Metrology
Overview of Traditional Metrology Methods
Traditional metrology relies on manual tools and techniques to measure and inspect objects. You might recognize tools like calipers, micrometers, and coordinate measuring machines (CMMs). These methods often require skilled operators to handle the equipment and interpret the results. While they have been reliable for decades, they come with limitations. Manual processes are time-consuming and prone to human error, especially when dealing with complex geometries or delicate materials.
For example, a CMM uses a physical probe to touch the surface of an object and record its dimensions. This contact-based approach can damage fragile materials or fail to capture intricate details. Additionally, traditional methods struggle to keep up with the speed and precision demands of modern manufacturing.
Key Differences in Speed, Accuracy, and Automation
When comparing traditional metrology to automated vision metrology, the differences are striking. Automated systems use advanced imaging and software to perform measurements without physical contact. This approach enhances speed, accuracy, and automation capabilities.
- Speed: Automated measurement routines significantly increase inspection speed. Unlike manual methods, which require time-intensive setups, automated systems can process multiple parts in seconds. For instance, video edge detection eliminates the need for manual alignment, saving valuable time.
- Accuracy: Automated vision metrology reduces human error by relying on precise algorithms. Systems like the Starrett AV450 combine manual and automated measurements, ensuring flexibility while maintaining high accuracy.
- Automation: Traditional methods offer limited automation. In contrast, automated systems provide real-time data for analysis and improvements. User-friendly interfaces and automated routines make these systems accessible even to operators with minimal training.
| Feature | Traditional Metrology | Automated Vision Metrology |
|---|---|---|
| Inspection Speed | Slower due to manual processes | Increased speed and throughput |
| Accuracy | Subject to human error | Enhanced accuracy through automation |
| Automation Capability | Limited | High, with user-friendly interfaces |
By adopting automated metrology, you can enhance product quality, reduce waste, and streamline your quality control processes.
Advantages of Non-Contact Inspection
Non-contact vision inspection offers several advantages over traditional contact-based methods. These systems use cameras, lasers, or other imaging technologies to measure objects without touching them. This approach is ideal for materials that are fragile, elastic, or sensitive to pressure.
- Non-contact systems prevent damage to delicate specimens during testing. For example, they can safely measure flexible materials like thin films or soft plastics.
- High-speed data acquisition captures a large number of points in a fraction of the time required by manual methods. This efficiency reduces inspection time and lowers manufacturing costs.
- These systems excel in high-extension tests, where traditional probes might cause specimen whiplash or sensor impairment.
Non-contact inspection also ensures precise measurements for complex geometries. By eliminating physical contact, you can achieve consistent results without risking damage to your products. This makes non-contact methods a cornerstone of modern automated vision metrology.
Advantages of Metrology Machine Vision Systems
Enhanced Speed and Efficiency
Metrology machine vision systems transform how you approach in-line metrology tasks. These systems use advanced imaging technologies, such as event-based imaging and AI-driven software, to speed up inspection processes. You can measure multiple parts in seconds, reducing bottlenecks in production lines.
Recent advancements in machine vision technologies have significantly improved industrial applications. For example, AI-powered systems analyze images faster than traditional methods, ensuring quicker quality control. This efficiency allows you to maintain high production rates without sacrificing precision.
Non-contact in-line metrology further enhances speed. By eliminating physical contact, these systems avoid delays caused by manual alignment or probe adjustments. This streamlined approach ensures faster measurements, even for complex geometries or delicate materials.
Improved Accuracy and Repeatability
Accuracy is critical in manufacturing. Metrology machine vision systems deliver consistent results by relying on precise algorithms and calibrated imaging tools. You can achieve repeatable measurements across multiple production cycles, ensuring product consistency.
These systems excel in detecting minute defects that traditional methods might overlook. For example, high-resolution cameras capture intricate details, enabling precise dimensional analysis. This capability ensures compliance with industry standards and reduces the risk of faulty products reaching customers.
Repeatability also improves with automated processes. By removing human intervention, you eliminate variability in measurements. This consistency builds trust in your quality control processes and enhances overall productivity.
Reduction in Human Error and Labor Costs
Manual inspections often lead to errors due to fatigue or misinterpretation. Metrology machine vision systems automate these tasks, reducing the likelihood of mistakes. You can rely on these systems to perform accurate inspections without constant supervision.
Automation also lowers labor costs. Instead of assigning skilled operators to repetitive tasks, you can allocate resources to more strategic roles. For example, automated systems handle in-line metrology tasks efficiently, freeing up your workforce for higher-value activities.
By reducing human error and labor costs, these systems improve operational efficiency. You can focus on optimizing production while maintaining high-quality standards.
Capability to handle complex geometries and delicate materials.
Metrology machine vision systems excel at inspecting objects with intricate shapes and fragile materials. These systems use advanced imaging technologies to capture precise measurements without physical contact. This makes them ideal for industries where traditional methods struggle to deliver accurate results.
You can rely on these systems to handle complex geometries with ease. For example, products with curved surfaces, sharp edges, or intricate patterns often pose challenges for manual tools. Vision systems, however, use high-resolution cameras and sophisticated algorithms to map every detail. This ensures accurate measurements, even for the most complicated designs.
Tip: If you work with delicate materials like glass, thin films, or soft plastics, non-contact inspection prevents damage during measurement.
Here are some key benefits of using metrology machine vision systems for complex and delicate tasks:
- Non-Contact Measurement: These systems avoid physical contact, reducing the risk of scratches or deformation.
- High Precision: Advanced optics and software ensure measurements are accurate to the micron level.
- Adaptability: They can measure objects of various sizes, shapes, and materials without requiring extensive setup changes.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Non-Contact Inspection | Prevents damage to fragile materials like glass or soft polymers. |
| 3D Imaging | Captures detailed surface profiles of complex geometries. |
| Flexible Configurations | Adapts to different shapes and sizes without manual adjustments. |
These capabilities make metrology machine vision systems indispensable for industries like aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. You can trust them to deliver consistent results, even when working with challenging materials or designs. By adopting this technology, you ensure precision and protect your products from unnecessary damage.
Applications of Automated Vision Metrology in Manufacturing
Ensuring Product Consistency and Compliance
Automated vision metrology plays a vital role in maintaining product consistency and ensuring compliance with industry standards. You can use these systems to perform precise measurements and inspections, reducing variability in production. For example, high-resolution cameras and advanced algorithms detect even the smallest defects, ensuring every product meets strict quality requirements.
These systems also simplify compliance with regulatory standards. By automating in-line metrology processes, you can record and analyze data in real time. This ensures your products consistently meet specifications, reducing the risk of recalls or customer dissatisfaction.
Note: Automated metrology systems automatically record measurement data in linked databases, making it easier to track quality trends and demonstrate compliance during audits.
Use in Industries Like Automotive, Aerospace, and Electronics
Automated vision metrology has widespread applications in industries like automotive, aerospace, and electronics. In automotive manufacturing, these systems enhance precision and speed, ensuring high-quality vehicle performance. For example:
- Hexagon's solutions measure over 15 dimensions of a long shaft in less than 20 seconds.
- They achieve a pitch diameter error range of less than ±20µm, even under challenging conditions like oil contamination.
In aerospace, automated metrology ensures the accuracy of critical components like turbine blades and fuselage assemblies. These systems measure roundness, cylindricity, and concentricity without physical contact, reducing the risk of damage.
Electronics manufacturers rely on automated vision metrology for defect detection and assembly verification. The technology supports the fast-growing electric vehicle sector by ensuring speed and quality in production.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Measurement Speed | Automatically measures multiple dimensions in seconds. |
| Measurement Accuracy | Maintains precision even under challenging conditions. |
| Data Management | Links measurement data with ERP/MES/SPC systems for streamlined analysis. |
Tasks Such as Dimensional Measurement, Defect Detection, and Assembly Verification
Automated vision metrology excels in tasks like dimensional measurement, defect detection, and assembly verification. You can rely on these systems to deliver accurate measurements with minimal error. For example, the average relative error for length and width measurements is 1.94% and 1.31%, respectively.
Defect detection is another critical application. These systems use metrics like precision and recall to identify flaws with high accuracy. For instance, the F1 score combines precision and recall, providing a reliable measure of system performance.
Assembly verification ensures components are correctly aligned and assembled. Automated systems use advanced imaging tools to verify assembly accuracy, reducing the risk of faulty products.
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | Measures the correctness of classifications, ensuring reliable defect detection. |
| Precision | Evaluates the accuracy of positive predictions, reducing false positives. |
| Recall | Assesses the ability to identify all instances of a defect, minimizing overlooked flaws. |
| F1 Score | Combines precision and recall into a single metric for overall performance evaluation. |
By leveraging automated vision metrology, you can streamline these tasks, improve quality control, and enhance production efficiency.
Future Potential of Metrology Machine Vision Systems
Integration of AI and Machine Learning
The integration of AI and machine learning is transforming metrology machine vision systems. These technologies enhance the ability to analyze data, detect patterns, and make predictions. You can expect systems to become smarter and more efficient as they learn from past inspections. For example, AI algorithms can identify defects that are too subtle for traditional methods.
The market for AI-driven metrology systems is growing rapidly. By 2024, it is projected to reach $12.72 billion, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.57%. By 2035, this market could expand to $25.6 billion.
| Year | Market Size (USD Billion) | CAGR (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 12.72 | 6.57 |
| 2035 | 25.6 |
This growth highlights the increasing demand for smarter, more capable systems. By adopting AI-powered solutions, you can improve accuracy, reduce downtime, and stay ahead in competitive industries.
Real-Time Monitoring and Predictive Maintenance
Real-time monitoring is revolutionizing how you maintain equipment and ensure operational efficiency. These systems use IoT sensors and machine learning to continuously track equipment health. They provide real-time data, allowing you to identify potential issues before they lead to failures.
Predictive maintenance is a key benefit of this technology. Instead of reacting to breakdowns, you can schedule maintenance based on actual equipment conditions. This approach reduces unexpected downtime and repair costs. It also enhances worker safety by addressing problems proactively.
- Continuous monitoring improves operational reliability.
- Real-time data processing identifies patterns that indicate potential failures.
- Optimized maintenance schedules reduce idle time and increase efficiency.
By implementing real-time inspection and monitoring systems, you can transition from reactive to predictive maintenance, saving time and resources.
Expanding Applications in Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
Metrology machine vision systems are playing a crucial role in smart manufacturing and Industry 4.0. These systems integrate seamlessly with IoT devices, smart sensors, and cloud-based platforms. This integration enhances data visibility and enables better decision-making.
| Measurable Outcome | Description |
|---|---|
| Smoother integration | Enhanced data visibility and better monitoring through integration with IoT devices and smart sensors. |
| Advanced data analytics and AI | Improved decision-making and optimized production schedules through predictive analytics and machine learning. |
| Expanded API support | Better integration with enterprise systems and third-party applications, enhancing overall efficiency. |
| Cloud-based systems | Scalability and centralized data management for enterprise-level reporting. |
| Enhanced security | Continuous updates to protect against cyber threats, ensuring data integrity. |
| Digitalization | Streamlined data entry and analysis by replacing manual processes with digital forms and instructions. |
These advancements allow you to streamline operations and improve productivity. By leveraging these technologies, you can achieve greater scalability, enhanced security, and more efficient workflows. The future of manufacturing lies in these smart, interconnected systems.
Metrology machine vision systems offer transformative benefits for modern manufacturing. They improve product quality, increase productivity, and reduce waste. By automating inspections, you can detect defects early, enhance accuracy, and maintain consistent performance.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improve product quality | Automated inspection enhances speed and accuracy, reducing defects before packaging or shipping. |
| Increase productivity | Machine vision systems accelerate operations and maintain performance throughout shifts. |
| Reduce waste | Identifies manufacturing flaws and overfill, leading to lower scrap rates and material costs. |
| Improve processes | Detects quality changes and records product lifecycle, aiding in continuous improvement. |
These systems also revolutionize quality control.
- Decreased inspection time speeds up production.
- Non-contact inspection prevents damage to sensitive materials.
- Enhanced productivity allows workers to focus on complex tasks.
Adopting this technology ensures precision, efficiency, and compliance with industry standards. You can stay competitive by integrating these systems into your processes.
FAQ
What industries benefit the most from metrology machine vision systems?
Metrology machine vision systems are widely used in industries like automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices. These sectors rely on precise measurements and defect detection to ensure product quality and compliance with strict standards.
How do these systems improve manufacturing efficiency?
They automate inspection tasks, reducing the time needed for manual measurements. You can process multiple parts simultaneously, identify defects early, and maintain consistent quality. This boosts production speed and minimizes waste.
Are metrology machine vision systems difficult to operate?
Modern systems feature user-friendly interfaces and automated processes. You can operate them with minimal training. Many systems also include intuitive software that simplifies setup and data analysis.
Can these systems handle fragile or complex materials?
Yes, they use non-contact inspection methods like lasers and cameras. This prevents damage to delicate materials such as glass or soft plastics. They also excel at measuring intricate geometries with high precision.
What is the role of AI in metrology machine vision systems?
AI enhances defect detection, data analysis, and predictive maintenance. It helps systems learn from past inspections, improving accuracy and efficiency over time. AI-driven systems also adapt to new challenges, making them smarter and more reliable.
See Also
Fundamentals of Barcode Scanning Using Vision Technology
An Overview of Cameras Used in Vision Systems
Understanding Image Processing in Machine Vision Applications
Essential Camera Resolution Concepts for Vision Systems
Comprehending Dimensional Measurements in Vision Technologies
