What Makes Pascal VOC Essential for Machine Vision?

The Pascal VOC machine vision system has become a vital tool in the field of machine vision. It supports crucial tasks like object detection and segmentation, enabling researchers to develop and refine algorithms. You might wonder why this system holds such importance. Its structured annotations and ease of use with machine learning models make it a trusted benchmark for evaluating performance. Over the years, researchers have accessed the dataset over 27,000 times, highlighting its widespread adoption. With an Altmetric score of 30, it has proven its academic influence and significance in advancing machine vision technologies.
Key Takeaways
- Pascal VOC is an important tool for computer vision. It gives clear labels for tasks like finding and cutting out objects.
- The dataset's detailed labels and fair scoring system make it great for testing AI models.
- Pascal VOC works for many tasks, like finding objects and sorting images. This makes it useful for scientists and developers.
- Its past importance and impact on newer datasets show its big role in improving computer vision.
- Using Pascal VOC can make models better, especially when used with harder datasets like COCO.
Understanding the Pascal VOC Dataset
What is the Pascal VOC Dataset?
The Pascal VOC dataset is one of the most influential resources in the field of machine vision. It provides a collection of annotated images designed to support tasks like object detection, image classification, and segmentation. This dataset includes a wide variety of objects, such as animals, vehicles, and household items, across 20 distinct categories. Its structured annotations make it easy for you to train and evaluate machine learning models effectively.
The dataset has been instrumental in shaping computer vision research. Between 2005 and 2012, the Pascal VOC challenges encouraged researchers to develop innovative algorithms. Among its versions, VOC07 and VOC12 are the most widely used. VOC12, for instance, contains 11,530 training images and 27,450 annotated objects. These numbers highlight its scale and utility in advancing machine vision tasks.
Key Features of the Pascal VOC Machine Vision System
The Pascal VOC machine vision system stands out due to its robust features. These features ensure that you can use it as a reliable benchmark for evaluating your models. Here are some of its key attributes:
- Comprehensive Annotations: Each image in the dataset includes detailed annotations, such as object bounding boxes, segmentation masks, and class labels. This allows you to tackle multiple tasks with the same dataset.
- Standardized Evaluation Metrics: The system uses metrics like Average Precision (AveP) to measure model performance. For example, AveP calculates precision at various recall levels, ensuring consistent and fair comparisons.
| Performance Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Average Precision (AveP) | Computed by averaging precision over a set of evenly spaced recall levels {0, 0.1, 0.2, ... 1.0}. It is defined as AveP = 1/11 ∑ r ∈ {0, 0.1, …, 1.0} p_interp(r), where p_interp(r) is the interpolated precision that takes the maximum precision over all recalls greater than r. |
- Versatility: The dataset supports various tasks, including object detection, segmentation, and classification. This versatility makes it a go-to resource for researchers and developers.
- Ease of Use: Its compatibility with popular machine learning frameworks ensures that you can integrate it seamlessly into your projects.
These features make the Pascal VOC machine vision system a cornerstone for advancing computer vision technologies.
Historical Significance in Machine Vision
The Pascal VOC dataset has played a pivotal role in the evolution of machine vision. Its challenges, held annually from 2005 to 2012, pushed researchers to improve object recognition algorithms. This dataset became a benchmark for evaluating new methods, fostering innovation in the field.
You can see its influence in the way it shaped subsequent datasets and research. The VOC challenges introduced standardized evaluation protocols, which are now widely adopted. Researchers often cite the dataset in their work, underscoring its importance. Its historical impact is evident in its contribution to tasks like object detection and image classification.
- The Pascal VOC dataset is recognized for advancing object recognition algorithms in machine vision.
- Researchers frequently reference it in academic papers, highlighting its influence on the field.
- Its historical context and challenges have inspired the development of newer datasets and evaluation methods.
The Pascal VOC dataset remains a testament to the progress made in machine vision. Its legacy continues to guide researchers and developers in their pursuit of better algorithms.
Technical Insights into Pascal VOC
Annotation Formats and Dataset Structure
The Pascal VOC dataset offers a well-organized structure that simplifies your work in object detection and image segmentation. Each image includes detailed annotations that describe the objects within it. These annotations contain essential information such as bounding box coordinates, object names, poses, and difficulty levels. For example:
- Filename: The relative path of the annotated image.
- Path: The absolute path of the output file after annotations.
- Size: Dimensions of the image, including height, width, and depth (e.g., RGB or grayscale).
- Object Details: Includes the name of the object, its pose (e.g., left or right orientation), whether it is truncated, and its difficulty level.
- Bounding Box: Specifies the top-left and bottom-right coordinates of the object.
This structured format ensures that you can train deep learning models effectively. Whether you are working on instance segmentation or semantic segmentation, the dataset provides the necessary details to achieve high accuracy in detection tasks.
Supported Tasks: Object Detection and Beyond
Pascal VOC supports a wide range of tasks, making it a versatile tool for your machine vision projects. While object detection remains its primary focus, the dataset also facilitates image segmentation, including both semantic and instance segmentation. Researchers have used it to benchmark object detection models like YOLO and R-CNN, achieving impressive results.
Empirical studies highlight its effectiveness in object detection tasks. For instance, benchmark evaluations show high localization accuracy and runtime efficiency:
| Method | Localization (PG) | Model Faithfulness (OA) | Runtime (Time) |
|---|---|---|---|
| D-CLOSE | 88.49% | 0.863 | 71.42s |
| G-CAME | 96.13% | 0.549 | 0.54s |
These results demonstrate the dataset's reliability in testing and improving object detection models.
Compatibility with Machine Learning Models
The Pascal VOC dataset integrates seamlessly with various machine learning frameworks, making it a preferred choice for researchers and developers. Its balanced object distribution ensures that deep learning models can learn effectively without bias. You can use it to train and evaluate models like YOLO, R-CNN, and others, achieving consistent performance across tasks like instance segmentation and semantic segmentation.
Benchmarking studies confirm its compatibility with modern object detection models. The dataset's annotations and structure align well with evaluation metrics, enabling you to test models efficiently. Whether you are working on deep learning or traditional methods, Pascal VOC provides a robust foundation for your projects.
Comparing Pascal VOC with Other Datasets

Pascal VOC vs. COCO: Key Differences
When comparing Pascal VOC to COCO, you notice distinct differences in their focus, structure, and use cases. Pascal VOC emphasizes typical scenes with a limited number of categories, while COCO excels in complex scene understanding with a broader range of categories. This distinction makes Pascal VOC ideal for tasks requiring simpler contexts, whereas COCO is better suited for advanced applications.
| Feature | PASCAL VOC | COCO |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Typical scenes with limited categories | Complex scene understanding with more categories |
| Object Categories | 20 classes (vehicles, household, animals, person) | More categories and instances per category |
| Image Source | Flickr, typically one or more objects per image | Non-iconic images with multiple objects |
| Generalization | Limited due to iconic views | Improved generalization with varied angles |
| Competition Impact | Significant contributions over seven years | Increased difficulty with smaller objects |
COCO's evaluation system is often considered the gold standard for computing Mean Average Precision (mAP). It provides a more detailed analysis of detection models, which leads to comprehensive results. For example, the YOLOv4 model achieved an Average Precision (AP) of 43.5% on COCO, outperforming typical metrics associated with Pascal VOC. However, Pascal VOC's simpler structure and fewer categories make it easier to use for beginners or for tasks requiring less complexity.
Strengths and Limitations of Pascal VOC
Pascal VOC has several strengths that make it a reliable benchmark for machine vision tasks. Its detailed annotations, including bounding boxes and segmentation masks, allow you to train models effectively. The dataset's smaller size reduces ambiguity, making it easier to interpret visual contexts. Additionally, its larger object scales simplify detection tasks compared to COCO's diverse and smaller object scales.
| Metric | Pascal VOC Performance | COCO Performance | Observations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Average Pearson Correlation (mAρ𝜌) | Higher | Lower | Models perform better on Pascal VOC due to less complex scenes and fewer categories per image. |
| Dataset Size | Smaller | Larger | Pascal VOC has a smaller dataset size, which may reduce ambiguity in visual contexts. |
| Object Scale | Larger | Smaller | Larger object scales in Pascal VOC aid in easier detection compared to COCO's diverse contexts. |
However, Pascal VOC also has limitations. Its smaller dataset size and limited categories restrict its ability to generalize across diverse scenarios. While its annotations are precise, they lack the richness of COCO's annotations, which include more detailed object relationships and contextual information. Despite these limitations, Pascal VOC remains a valuable tool for benchmarking simpler machine vision tasks.
Complementary Role of Pascal VOC in Machine Vision
Pascal VOC plays a complementary role alongside other benchmark datasets like COCO. By integrating Pascal VOC with more complex datasets, you can enhance model performance and achieve better results. For instance, the YOLO-RACE model demonstrated a significant improvement in mAP50 from 0.763 to 0.773 when using the full model on Pascal VOC. This integration highlights how Pascal VOC can strengthen machine vision systems by providing a simpler yet effective dataset for initial training.
The dataset's precision and recall metrics further emphasize its complementary role. Models trained on Pascal VOC achieved a precision of 0.785 and a recall of 0.699, outperforming others in mAP50 and mAP50@95. These results show that Pascal VOC can serve as a foundational dataset, enabling you to fine-tune models before applying them to more complex datasets like COCO.
Pascal VOC's simplicity and structured annotations make it an excellent starting point for researchers and developers. Its role in advancing machine vision lies in its ability to complement other datasets, providing a balanced approach to training and evaluation.
The Ongoing Relevance of Pascal VOC
Why Pascal VOC Remains a Benchmark
Pascal VOC continues to serve as a benchmark in machine vision due to its simplicity and effectiveness. Its structured annotations, including bounding boxes and segmentation masks, make it a reliable dataset for evaluating object classification methods. Researchers often use it to test deep learning techniques, as its smaller size allows for faster experimentation compared to larger datasets like COCO. This efficiency makes it ideal for prototyping and refining models.
The dataset's performance metrics, such as mean Intersection-over-Union (mIoU), highlight its robustness. For example, architectural features like atrous convolutions (AC) and ASPP modules significantly improve model performance on Pascal VOC. These results demonstrate the dataset's ability to benchmark models effectively, even against common corruptions. Its less complex nature compared to datasets like Cityscapes ensures consistent results, reinforcing its role as a foundational tool in machine vision.
Applications in Modern Object Detection Projects
Pascal VOC remains relevant in modern object detection projects. Its detailed annotations, including bounding boxes, segmentation masks, and object class recognition labels, support tasks like object detection, segmentation, and classification. Models like YOLO and R-CNN frequently use Pascal VOC for training and evaluation, achieving high accuracy in detecting objects across various categories.
The dataset's versatility extends to other applications, such as image segmentation and object classification methods. For instance, VOC2007 is still widely used for training classifiers and detectors. Its compatibility with deep learning techniques ensures seamless integration into modern workflows. The dataset's structured format and standardized evaluation metrics make it a go-to resource for researchers aiming to improve model performance.
| Dataset | Purpose |
|---|---|
| VOC2007 | Training image classifiers and object detectors |
| ImageNet | Training image classifiers |
| COCO | Object detection tasks |
| OpenImages v7 | Image classification and object detection |
This table illustrates how Pascal VOC complements other datasets in advancing machine vision tasks.
Future Potential of the Pascal VOC Dataset
The future of Pascal VOC lies in its adaptability. While newer datasets like COCO and OpenImages offer more complexity, Pascal VOC's simplicity makes it an excellent starting point for beginners. Its structured annotations and bounding boxes provide a solid foundation for training models in object detection and segmentation.
Researchers can also use Pascal VOC to explore hybrid approaches. Combining it with larger datasets can enhance model performance by leveraging the strengths of both. For example, models trained on Pascal VOC often achieve higher precision and recall when fine-tuned on more complex datasets. This complementary role ensures its continued relevance in machine vision.
Pascal VOC's legacy as a benchmark dataset will likely persist. Its ability to support diverse tasks, from object detection to segmentation, ensures its place in the evolving landscape of machine vision.
Pascal VOC has shaped machine vision by offering a reliable dataset with structured annotations and standardized metrics. Its simplicity and adaptability make it a cornerstone for tasks like object detection and segmentation. Over the years, its impact has grown, as shown in the dataset's evolution:
| Dataset | Number of Images | Number of Annotated Images | Object Categories | Annotated Objects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VOC2007 | 9,963 | 9,963 | 20 Classes | 24,640 |
| VOC2012 | 11,530 | 11,530 | 20 Classes | 28,000 |
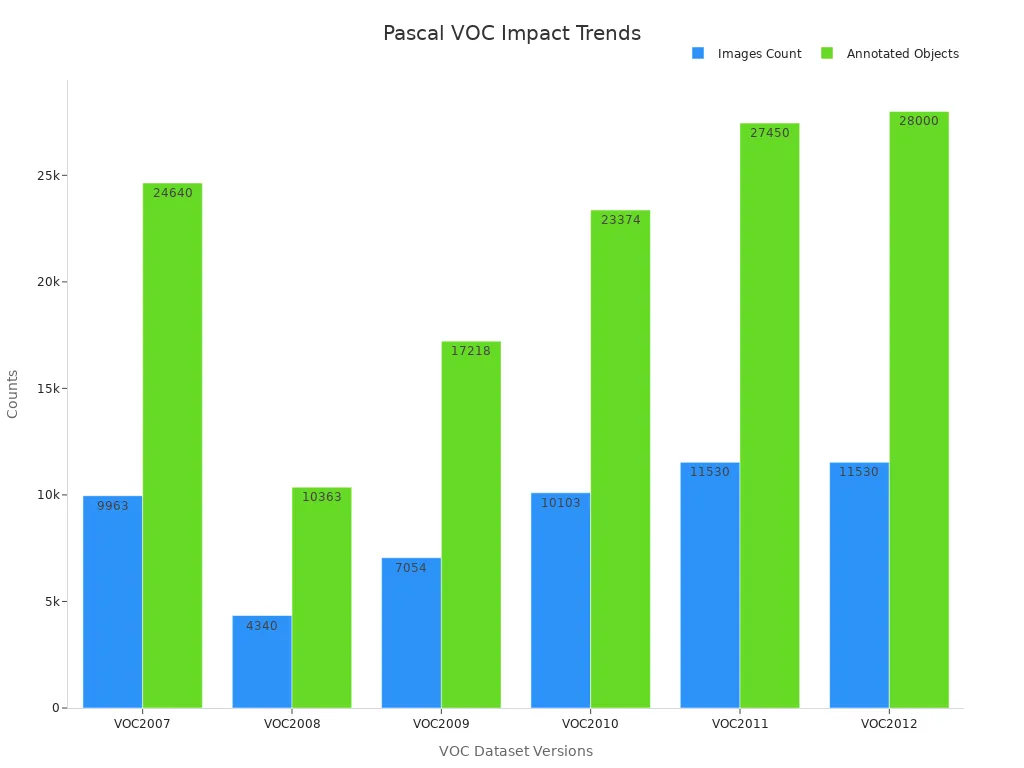
As machine vision evolves, you can rely on Pascal VOC as a foundational tool for innovation and benchmarking. Its legacy continues to inspire advancements in the field.
FAQ
What is the primary purpose of the Pascal VOC dataset?
The Pascal VOC dataset helps you train and evaluate machine vision models. It provides structured annotations for tasks like object detection, segmentation, and classification. Its simplicity and versatility make it a reliable resource for researchers and developers.
How does Pascal VOC differ from other datasets?
Pascal VOC focuses on typical scenes with fewer categories, making it easier for you to work with. Unlike COCO, which includes complex scenes and smaller objects, Pascal VOC simplifies object detection tasks with larger object scales and fewer annotations.
Can Pascal VOC be used with modern machine learning models?
Yes, you can use Pascal VOC with modern models like YOLO and R-CNN. Its structured annotations and compatibility with machine learning frameworks ensure seamless integration into your projects, whether for object detection or segmentation tasks.
Why is Pascal VOC still relevant today?
Pascal VOC remains relevant because of its simplicity and historical significance. You can use it as a benchmark for testing algorithms or as a starting point for training models before moving to more complex datasets like COCO.
What are the key features of Pascal VOC annotations?
Pascal VOC annotations include bounding boxes, segmentation masks, and class labels. These features allow you to identify and classify objects in images effectively. The dataset also provides details like object poses and difficulty levels, enhancing its utility for machine vision tasks.
See Also
Understanding The Importance Of Triggering In Machine Vision
Exploring Pixel-Based Machine Vision For Contemporary Uses
A Comprehensive Guide To Image Processing In Machine Vision
